Lettuce is a versatile and nutritious leafy green that can be grown easily in your own backyard or even indoors. Whether you are a gardening enthusiast or a beginner, this guide will provide you with all the information you need to successfully grow your own lettuce. From seed selection to harvest, we will cover every step of the process, so let’s get started!
When to Start Lettuce
The first step in growing lettuce is knowing when to start. Lettuce is a cool-season crop that prefers temperatures between 45°F (7°C) and 75°F (24°C). It thrives in the early spring and fall, as it tends to bolt and become bitter in the heat of the summer. So, depending on your climate, you can start lettuce as early as late winter or as late as early fall.
For those living in regions with milder winters, starting lettuce in late winter can be a great way to get a head start on the growing season. By sowing seeds indoors or in a greenhouse, you can transplant seedlings outdoors once the soil warms up. This method allows you to enjoy fresh, homegrown lettuce earlier than if you were to wait for the traditional spring planting time.
On the other hand, if you reside in an area with scorching summers, starting lettuce in early fall can ensure a bountiful harvest. The cooler temperatures and shorter days of autumn create ideal conditions for lettuce to thrive without the risk of bolting. By planting in late summer or early fall, you can extend your growing season and continue to enjoy crisp, flavorful lettuce well into the cooler months.
How to Grow Lettuce From Seed
Growing lettuce from seed is simple and economical. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose a variety of lettuce that suits your taste preferences and growing conditions.
- Prepare a seed starting tray or small pots with a well-draining seed starting mix.
- Sow the lettuce seeds, following the packet instructions for depth and spacing.
- Lightly water the seeds and cover the tray or pots with a plastic dome or plastic wrap.
- Place the tray or pots in a warm location with indirect sunlight.
- Keep the soil consistently moist by misting it with water.
- After the seeds germinate, remove the plastic cover and move the tray or pots to a location with bright, indirect light.
- When the lettuce seedlings have developed two to three true leaves, they are ready to be transplanted.
Expanding on the process, it’s important to note that lettuce is a cool-season crop that thrives in temperatures between 45°F and 75°F (7°C to 24°C). If you live in a region with hot summers, consider planting lettuce in partial shade to prevent it from bolting prematurely. Additionally, incorporating organic matter like compost into the soil before planting can provide essential nutrients for healthy lettuce growth.Once your lettuce seedlings are ready for transplanting, choose a location in your garden with well-draining soil and ample sunlight. Dig small holes spaced according to the mature size of the lettuce variety you’re growing, typically 6 to 12 inches apart. Gently remove the seedlings from the seed starting tray or pots, being careful not to disturb the roots, and place them in the prepared holes. Water the transplanted seedlings thoroughly to help them establish in their new environment.
How and When to Transplant Lettuce
Transplanting lettuce seedlings is essential for proper spacing and growth. Here’s how to do it:
Transplanting lettuce seedlings is a crucial step in ensuring a bountiful harvest of fresh, crisp lettuce leaves. By carefully moving the young plants from their nursery environment to the garden bed, you give them the space and nutrients they need to thrive.
- Prepare the planting area by loosening the soil and removing any weeds.
- Water the seedlings thoroughly before transplanting.
- Using a trowel or your hands, dig a hole for each seedling, making sure it’s slightly larger than the root ball.
- Carefully remove the seedling from the tray or pot, gently loosening the roots if necessary.
- Place the seedling in the hole, ensuring that the base of the lettuce plant is level with the soil surface.
- Backfill the hole with soil and gently firm it around the seedling.
- Water the transplanted lettuce thoroughly and keep the soil consistently moist.
It is best to transplant lettuce seedlings in the early morning or late afternoon to minimize stress on the plants. This timing allows the lettuce to adjust to its new surroundings before facing the heat of the day. Additionally, choosing a slightly overcast day for transplanting can help reduce the shock to the seedlings.
How to Plant Lettuce – Spacing and Patterns
Proper spacing is crucial for healthy lettuce plants. Here are some guidelines:
- For loose-leaf lettuce varieties, space the plants 6 to 10 inches apart.
- For head lettuce varieties, space the plants 12 to 18 inches apart.
- Consider interplanting lettuce with other cool-season crops, such as radishes or carrots, to maximize space.
- Use the “cut and come again” method for continuous harvesting. As the outer leaves of each plant mature, harvest them gently, leaving the inner leaves to grow.
When planting lettuce, it’s important to consider the microclimate of your garden. Lettuce thrives in cooler temperatures, so be mindful of the amount of sunlight your lettuce plants will receive. In hot climates, providing afternoon shade can help prevent lettuce from bolting prematurely.
Additionally, lettuce is a heavy feeder, meaning it requires a nutrient-rich soil to grow successfully. Before planting, amend your soil with compost or well-rotted manure to ensure your lettuce plants have access to the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. Consider using a balanced organic fertilizer throughout the growing season to support vigorous leaf production.
How Long to Grow Lettuce
The length of time it takes to grow lettuce depends on the variety and growing conditions. Typically, lettuce can be harvested within 45 to 60 days after sowing the seeds. However, if you prefer baby lettuce or leafy greens, you can start harvesting as early as 25 to 30 days after sowing.
When growing lettuce, it’s important to consider the temperature and sunlight exposure. Lettuce is a cool-season crop that thrives in temperatures between 45°F and 75°F. In hotter climates, providing shade or planting lettuce where it can receive partial sunlight can help prevent the leaves from becoming bitter and bolting prematurely.
Another factor to keep in mind when growing lettuce is soil quality. Lettuce prefers well-draining, fertile soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0. Adding compost or aged manure to the soil before planting can help improve its texture and nutrient content, leading to healthier and more flavorful lettuce leaves.
How to Water Lettuce
Proper watering is essential for healthy lettuce plants. Here are some watering tips:
- Water consistently to keep the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged.
- Avoid overhead watering to prevent leaf diseases. Instead, water at the base of the plants.
- Consider using a drip irrigation system or a soaker hose to deliver water directly to the roots.
- Water early in the day to allow the leaves to dry before evening.
Another important aspect to consider when watering lettuce is the temperature of the water. Lettuce plants prefer lukewarm water, as cold water can shock the roots and hinder nutrient absorption. It’s best to let the water sit out for a bit to reach room temperature before watering your lettuce plants.
Furthermore, the frequency of watering can vary depending on the weather conditions and the stage of growth of your lettuce. During hot and dry periods, you may need to water more frequently to prevent wilting. On the other hand, overwatering during cooler and wetter seasons can lead to root rot. It’s crucial to observe your plants closely and adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
How to Fertilize Lettuce
Lettuce is a light feeder and doesn’t require heavy fertilization. Here are some tips for fertilizing lettuce:
- Before planting, incorporate compost into the soil to improve its fertility.
- Apply a balanced organic fertilizer, following the package instructions for dosage.
- Avoid excessive nitrogen fertilization, as it can cause the lettuce plants to produce more leaves and less heart.
Sunlight Requirements for Lettuce
Lettuce prefers cooler temperatures and partial shade, especially in regions with hot summers. Here are some sunlight requirements:
- Provide at least 4 to 6 hours of direct sunlight for optimal growth.
- In hot climates, provide afternoon shade to protect the lettuce plants from scorching.
- Consider using shade cloth or planting lettuce in the shadow of taller plants.
Soil Requirements for Lettuce
Lettuce thrives in well-draining soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH. Here are some soil requirements:
- Choose a loamy soil with good organic matter content.
- Ensure the soil is loose and friable for proper root development.
- Avoid heavy clay soils that can become waterlogged.
- If needed, amend the soil with compost or well-rotted manure to improve its structure and fertility.
How to Grow Lettuce Outdoors
Growing lettuce outdoors is a rewarding experience. Here are some tips to help you succeed:
- Choose varieties that are suitable for your climate and the time of year.
- Prepare the soil by removing weeds and incorporating organic matter.
- Sow the seeds directly in the garden, following the packet instructions for spacing and depth.
- Keep the soil consistently moist during germination and establishment.
- Thin the seedlings to the recommended spacing when they reach a couple of inches in height.
- Protect the lettuce plants from extreme temperatures, pests, and diseases using appropriate preventive measures.
How to Grow Lettuce Indoors
If outdoor gardening is not an option, you can still enjoy fresh lettuce by growing it indoors. Here’s how:
- Choose a bright spot near a window that receives at least 4 to 6 hours of indirect sunlight per day.
- If natural light is limited, consider using a grow light to supplement the light requirements.
- Select a container or pots with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
- Fill the containers with a well-draining potting mix.
- Sow the lettuce seeds, following the packet instructions for spacing and depth.
- Water the soil lightly, keeping it consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Fertilize the lettuce plants with a balanced liquid fertilizer, following the package instructions for dosage.
- Harvest the lettuce leaves as they reach the desired size, leaving the inner leaves to continue growing.
How to Grow Lettuce In Containers and Pots
Growing lettuce in containers and pots is a space-saving option that allows you to enjoy fresh greens on your balcony or patio. Here’s how to do it:
- Select containers or pots with a depth of at least 6 inches and a diameter of 10 inches or more.
- Ensure the containers have drainage holes to prevent waterlogged soil.
- Fill the containers with a well-draining potting mix.
- Sow the lettuce seeds, following the packet instructions for spacing and depth.
- Water the soil lightly, keeping it consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Place the containers in a location that receives 4 to 6 hours of direct sunlight per day.
- Harvest the outer leaves as needed, allowing the inner leaves to continue growing.
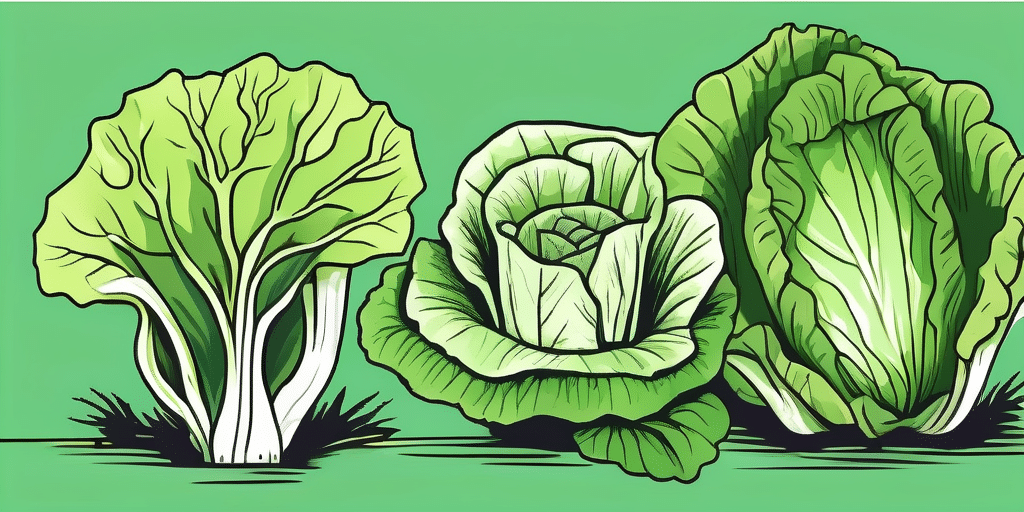
Best and Most Popular Lettuce Varieties
There are numerous lettuce varieties available, each with its own unique flavor, texture, and color. Here are some of the best and most popular choices:
- Romaine Lettuce: Known for its crunchy texture and slightly bitter taste, romaine lettuce is a staple in Caesar salads.
- Bibb Lettuce: Also known as butterhead lettuce, bibb lettuce has tender leaves and a sweet, buttery flavor.
- Iceberg Lettuce: Despite its reputation as a bland lettuce, iceberg lettuce can be refreshing and crispy when paired with flavorful ingredients.
- Leaf Lettuce: Leaf lettuce comes in various colors and forms, including green, red, and oakleaf. It has a mild flavor and is perfect for salads.
- Arugula: Although technically not a lettuce, arugula is a popular leafy green with a peppery taste that adds a zing to salads and sandwiches.
Lettuce Companion Plants – What to Plant With & Not Plant With Lettuce
Companion planting can help improve the growth and flavor of lettuce while deterring pests. Here are some suitable companion plants:
- Carrots: Carrots help loosen the soil for lettuce and provide shade to prevent the soil from drying out quickly.
- Radishes: Planting radishes alongside lettuce can help deter pests, such as aphids and flea beetles.
- Herbs: Certain herbs, like dill, cilantro, and chives, can attract beneficial insects that prey on lettuce pests.
On the other hand, there are some plants that should be avoided as they may compete for resources or attract pests:
- Brassicas: Avoid planting lettuce near cabbage, broccoli, or other Brassica family members, as they can attract similar pests.
- Onions: Onions can stunt the growth of lettuce, so it’s best to keep them separate.
Common Lettuce Pests and Diseases
Lettuce can be susceptible to certain pests and diseases. Here are some common ones to watch out for:
- Aphids: These tiny green insects can suck the sap from lettuce leaves, causing them to curl and distort.
- Slugs and Snails: These slimy pests can leave holes in lettuce leaves overnight.
- Fungal Diseases: Lettuce can be affected by diseases such as powdery mildew and downy mildew, which can cause white or grayish patches on the leaves.
To prevent and manage these issues, make sure to practice good garden hygiene, provide proper spacing, and monitor your plants regularly. Consider using organic pest control methods or consulting local agricultural extensions for specific recommendations.
How & When to Harvest Lettuce
Harvesting lettuce at the right time is essential for the best flavor and texture. Here’s how and when to do it:
- For loose-leaf lettuce varieties, you can harvest the outer leaves as soon as they reach a size you desire.
- For head lettuce varieties, wait until the heads are firm and solid.
- Avoid waiting too long to harvest, as lettuce can become bitter and tough.
- Using a sharp knife or scissors, cut the lettuce leaves at the base, leaving the center intact for further growth.
How to Store & Preserve Lettuce
To prolong the freshness of harvested lettuce, proper storage is essential. Here’s how to store and preserve lettuce:
- Before storing, remove any damaged or wilted leaves.
- Wash the lettuce leaves gently and pat them dry with a clean towel.
- Place the leaves in a resealable plastic bag or airtight container lined with paper towels.
- Store the lettuce in the refrigerator’s crisper drawer, where the temperature is cool and the humidity is high.
- Lettuce can stay fresh for up to a week when stored properly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about growing lettuce:
- Q: How often should I water lettuce?
- A: Lettuce prefers consistent moisture, so water whenever the top inch of soil feels dry.
- Q: Can I grow lettuce in a shady area?
- A: Lettuce needs at least 4 to 6 hours of sunlight per day, but it can tolerate partial shade.
- Q: Can I grow lettuce from the cuttings or regrow the cut ends?
- A: While some other vegetables can be regrown, lettuce is best grown from seeds for optimal results.
Now that you have all the knowledge required, it’s time to put it into action and grow your own lettuce. Enjoy the satisfaction of harvesting fresh, nutritious greens from your garden or windowsill. Happy lettuce growing!
Join Our Green-Thumbed Community!
Ready to transform your thumb into a vibrant shade of green? Subscribe for free to How to Grow Everything and receive tailor-made gardening wisdom that will help you build the garden of your dreams! Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting, our personalized advice, based on your specific location, grow zone, and interests, will guide you every step of the way. No spam, just the best gardening tips, special offers, and deals delivered straight to your inbox. Join our family of gardening enthusiasts and watch your garden—and your knowledge of lettuce growing—flourish!