
Welcome to my comprehensive guide on how to grow tomatoes. I've been growing tomatoes for many years and each year I learn something new. Although tomatoes are easy plants to grow, don't be discouraged if you run into some setbacks when you are first starting out. Every gardener I know, beginner or expert, experiences a new challenge each year. The key is to learn from your past mistakes and try again next year!
Tomatoes are the star of my garden and spend a great deal of time making sure that I get a bumper crop harvest of big, juicy, beautiful tomatoes. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced gardener, this article will provide you with all the essential information you need to successfully grow your own delicious tomatoes. This guide covers everything from understanding the basics of tomato growing, pruning, and maintaining your plants, all the way to harvesting and storing your tomatoes. Let's get started!
Snapshot: How to Grow Tomatoes
Types of Tomatoes:
Determinate and Indeterminate
When to Plant:
Start seeds indoors 7-8 weeks before your zones last frost date. Transplant outdoors after all danger of frost has passed and soil temps are above 50F.
How to Plant:
Transplant tomato plants in a deep hole amended with mycorrhizae, 1 tablespoon of Epsom salts, and worm castings for best results. For a stronger root system, plant up to 2/3rd of the plant itself underground (making sure to prune away lower branches so only the main stem is underground).
Plant Spacing:
Plant tomato plants approximately 12 inches apart (or one tomato plant per square foot).
Germination:
Under appropriate conditions, healthy tomato seeds should germinate within 5-10 days of sowing.
Best Soil:
Nutrient rich, well-draining, slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0-6.8) with soil temperatures above 70F degrees. Tomatoes do best with soils with moderate levels of nitrogen (N) and high in phosphorus (P) and potassium (K).
Watering:
Moderate and consistent watering during the growing phase and less watering during the harvest phase (this prevents fruit cracking).
Sunlight:
Tomatoes love the sun! Provide 8 hours+ of full daily sunlight.
Fertilizer:
Tomatoes do well in soils amended with Epsom salt (magnesium), fish fertilizer, and compost.
Companion Plants:
Best tomato companion plants are basil, carrots, marigolds, and nasturtiums. Worst companions include brassicas (e.g. cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, etc.) sunflowers, peppers, eggplant, potatoes, and fennel.
Harvesting:
Harvest tomatoes as early as "first blush" or "breaker stage" (50% ripe) and allow to ripen inside. Alternatively, harvest when full-colored and vine ripened.
Tomato Basics: Know Before You Grow
Before we get started, it is important to understand some basic information about tomatoes. Tomatoes are the quintessential hot weather plants and cannot handle frost or very cool temperatures for very long. If you have a short growing season, this means that you'll have to either start your tomato seeds indoors during the winter months or purchase tomato starts/transplants. Additionally, there are many varieties of tomatoes which have different growing needs.
Check out the list of tomato types and considerations below before purchasing any tomato seeds or plants.
Determinate vs Indeterminate Tomatoes:
Determinate tomatoes are plants which will grow to a specific height and no more. These are compact plants that can easily be grown in pots and garden beds without having to worry about pruning or trellising. Indeterminate tomato plants are just that, they have no final height and will continue to grow and produce flowers until the plant finally dies with the first fall frost. Indeterminate tomatoes are very large plants which can quickly turn your garden space into a jungle. Unless you have a very large garden space, indeterminate tomato plants must be pruned and trellised.
Colors of Tomatoes:
Tomatoes come in a wide variety of colors. Harvesting a bounty of red, green, yellow, orange, striped, and purple tomatoes is half the fun of growing tomatoes to begin with. For the most part, the color of the tomato doesn't affect the way that it grows--and you can pretty much treat tomato plants of all colors the same. However, there may be slight nutritional differences. For example, dark purple or black tomatoes are claimed to be higher in antioxidants than other tomatoes.
Sauce vs Slicing Tomatoes:
Do you dream of making delicious homemade pasta sauces or tomato paste with your tomato harvest? Then, you'll want to grow "sauce" or "paste" tomato varieties like roma, san marzano, or Amish paste tomatoes. These tomatoes have a meatier texture and perfect flavor for making sauces. For salads or sandwiches, you'll want to grow a "slicer" tomato variety like brandywine, beefsteak, or Italian heirloom costoluto tomatoes. These tomatoes are large, flavorful, and are best for fresh eating. Now, you can always make a salad using paste tomatoes or pasta sauce with slicer tomatoes, but you'll get better results using each variety for their designated purpose.
Micro vs Cherry vs Full-Sized Tomatoes:
Tomatoes also come in a variety of different sizes. Micro tomatoes, such as "spoon tomatoes", are the smallest variety and are often smaller than blueberries! These are perfect as garnishes for salads and other dishes. Cherry tomatoes are a bit bigger, usually the size of a quarter, and are more versatile than micro tomatoes. Full-sized tomatoes are your standard tomato that you'd find on top of a burger. Now, just because a plant grows "micro" tomatoes or "cherry" tomatoes does not mean that the plant itself will be small. Some of the largest and most unwieldy tomato plants I have ever grown were micro tomatoes!
Choosing which tomato varieties to grow each year is a tough job. There are so many amazing tomatoes in all shapes, colors, and sizes that I pretty much always grow too many tomatoes. The best advice I can offer to beginners is to select 1 or 2 different kinds of tomatoes to grow each year until you get the hang of it. This will reduce your workload, focus your effort, make troubleshooting problems easier, and reduce the amount of labor dedicated to harvesting and processing your bounty.
Getting Started: Seeds vs Plants
Tomatoes can easily be grown from seed or by buying already established tomato plants to transplant into your garden. The difference really comes down to price, labor, and your preference of variety. Starting tomatoes by seed is definitely the most cost effective option. A pack of tomato seeds can cost as low as $2 for dozens of seeds. However, starting plants from seed is a more labor-intensive process which requires weeks of care and maintenance before your plants will be ready to transplant into your garden.
Buying tomato plants is a great option for those who want to get a jumpstart on the gardening season without having to dedicate a great deal of time to starting tomatoes from seed. Simply buy the plant and put it into your garden. Easy! The downside of buying transplants is that they tend to be more expensive ($5-$10 per plant) than purchasing seeds. Additionally, local nurseries or plant shops only tend to only carry a few common varieties of tomatoes. Thus, if you are interested in growing rare varieties, you won't find those types available for sale as plants.
Personally, I advise anyone just starting out to buy established tomato plants from a local nursery. This is a much easier way to get started. Once you get the hang of growing tomato plants, you can then transition into growing your own tomato plants from seed.
How to Grow Tomatoes from Seed

You have two options when it comes to growing tomato plants from seed.: indoors or direct-sow. While direct sow (i.e. planting the seeds directly in the garden in late spring) is the easiest method, some growing seasons are not long enough to allow for the plants to fully develop before harvest. In most grow zones, tomatoes should be started from seed to guarantee a good crop from your tomato plants before first frost.
Start Early:
In zones 3-8, it is best to start your seeds indoors about 6-8 weeks before your zone's last frost date. For many, that means starting your tomato seeds in the winter and early spring months of February, March, and April.
Have the Right Equipment:
To start seeds indoors you will need a seed tray, a warming seedling starter mat, seed starting mix, labels, and a grow light. These do not have to be fancy or expensive. Seeds are not picky and will germinate so long as they have water, soil, warmth, and a light source.
Sow & Wait Patiently:
Figure out how many tomato seeds you will be sowing (I always plant at least 2 more seeds of each variety than I need just in case some seeds do not germinate). Take a bowl and fill it with seed starting mix and add enough water to moisten the mixture. Fill your seed tray with the moistened seed starting mix, one cell for each seed you plan to start. Plant 1 tomato seed 1/2 inch deep in each cell and label each cell with the name of that variety. Place the seed starting tray on top of your seedling heat mat and under your grow light. Keep the light on for at least 8 hours per day and always keep the heat mat turned on. Each day, check the moisture level of your seed trays. You may need to water or gently mist your trays daily to maintain a nice moist environment. Within 5-10 days, your tomato seedlings should begin to sprout!
Pot Up Until Ready:
As seedlings emerge and begin to grow, identify your strongest plants and pot them up from cell packs into individual pots. You'll want to wait until your plants are at least 3-4" tall before doing this. Gently remove the plant, soil, and roots from the seed tray and place it in a small pot about 3-4" in diameter that has been prefilled with moistened soil. This is called "potting up" your tomato seedlings. Continue potting up your seedlings as they begin to out-grow their existing pot. Once your last frost date has passed, it is time to prepare to transplant your tomato plants outdoors!
- Sun Gro: Black Gold Organic Seedling Starter Mix: A light, fluffy, organic seedling starting mix that allows seedlings to get the light they need to germinate.
- Seed Starter Tray with Humidity Dome: An all-in-one seed starting set complete with humidity dome for early germinating.
- Seedling Starting Heat Mat: Germinate your tomato seeds fast by keeping their soil at the perfect temperature with a easy-to-use heat mat.
- Indoor LED Grow Lights: Tomato seeds need light for germination. These easy-to-install indoor LED grow lights can be used to ensure successful germination in any lighting environment.
Transplanting Tomatoes
Whether you've started your tomatoes from seed or purchased transplants, the best time to transplant your tomato plants outdoors is after your zone's last frost date. Patience is key here: cold temperatures can stunt your tomato plant's growth and frost can kill the plant completely. Wait until night time temperatures are consistently above 40F before planting tomatoes outside.
Tomato plants can be planted in raised garden beds, containers, and in-ground gardens. This section covers the process of actually planting your tomato plants into the ground, but you'll still need to continue reading to learn more about plant spacing, companion plants, and on-going plant care.
Pick a Location:
Tomatoes need full sun and fertile soil to grow. Find a spot in your garden that gets the most sun and warmth throughout the day. Also, depending on whether you chose determinate or indeterminate plants, make sure that your tomatoes have enough space to grow. You'll need to trellis or cage indeterminate plants else they will literally take over your garden bed.
Amend the Soil:
Prepare your tomato bed by adding nutrient dense amendments such as compost, aged manure, fish emulsion, worm tea, and/or a general all-purpose vegetable fertilizer. Tomato plants need a lot of nutrients to grow, so make sure that your soil is rich and fertile. For an extra boost, add 1 tablespoon of Epsom Salts (a source of magnesium) and a dash of mycorrhizae (for strong roots and nutrient uptake) to each individual tomato planting hole.
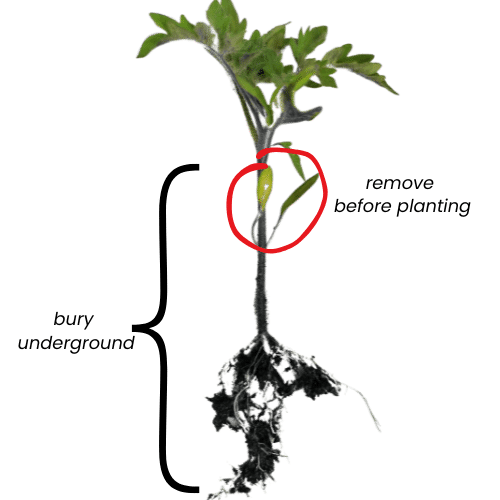
Prepare the Plant:
Tomato plants benefit from being planted deeply into the ground. As much as 2/3rds of the plant can be buried underground when transplanting (refer to the image above). Remove all lower leaves on the main stem (you don't want to bury any branches and leaves, just the main stem), and bury as much of the main stem as reasonable.
Water Thoroughly:
Once your tomato plant is in the ground, water the ground gently but thoroughly. Make sure that the soil is moist but stop watering before your soil turns into oversoaked mud.
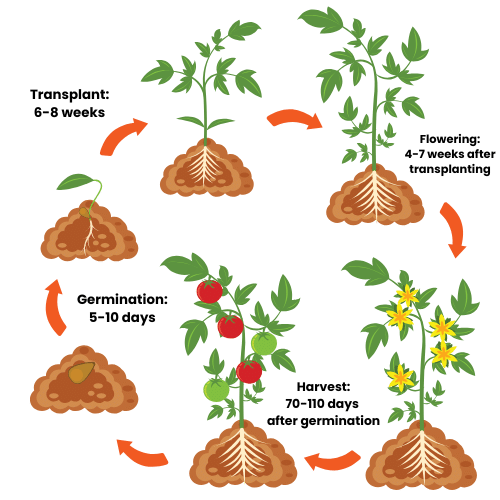
How Long Does it Take for Tomatoes to Grow?
Tomato plants need a long growing season to reach maturity and begin producing fruit. Just how long your specific tomato plant will take to reach maturity depends on the variety. Check the seed packet of each tomato variety for more information on maturity dates for your tomato seeds. In general, tomato plants reach maturity within 70-110 days. Determinate tomato types will produce a large crop of tomatoes all at once and then stop producing for the year. Indeterminate tomato types will continue to produce fruit all the way up to first frost.
Tomato Plant Spacing
Tomato plants should be spaced a minimum of 12 inches apart (or one per square foot). After years of growing tomatoes and getting overwhelmed by their growth rate and sprawling behavior, I learned to space my tomatoes 24 inches apart. This allows for better airflow, more space for me to manage and prune each plant, and healthier plants overall. The exception to this rule is if you are growing smaller determinate tomato plants. In this case, one plant per square foot is totally manageable.
Growing Tomatoes in Pots and Containers
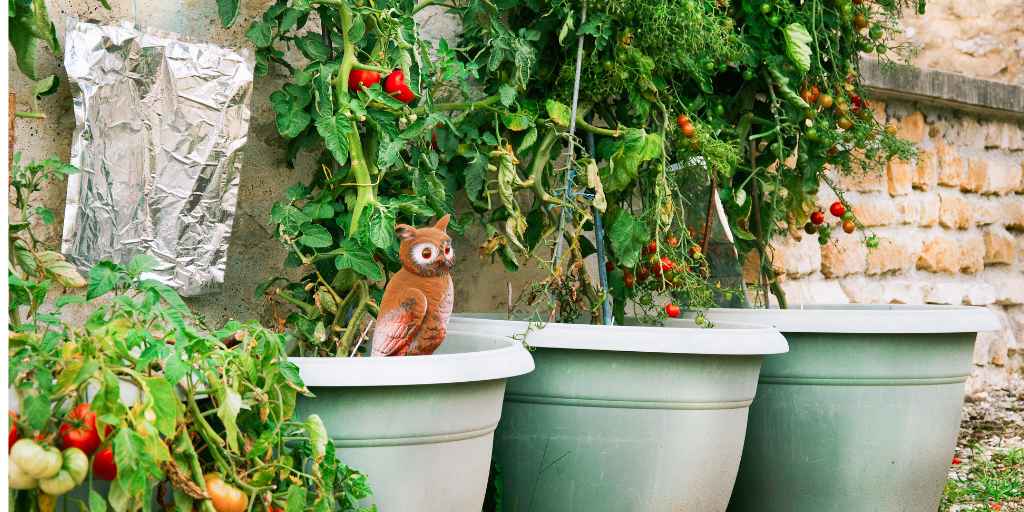

Tomatoes can absolutely be grown in containers and pots, but they will need more maintenance than tomatoes grown in-ground or in larger garden beds. Tomato plants need consistent watering and very fertile soil to produce their best fruit. With that said, it can be done! Each year, I grow a few "fun" varieties of tomatoes in containers on my back deck as a test to see if I should add that variety to my main garden. Follow the tips below and you should have no trouble growing tomatoes in pots!
Choose The Right Sized Pots:
Tomato plants, especially indeterminate varieties, need a lot of space and nutrients to fully flourish. If you are growing a smaller, determinate tomato variety, then you can get away with using one 12-18 inch diameter pot per plant for your tomatoes. For larger, indeterminate plants, you're going to need at least one 10-25 gallon pot per plant. I've tried growing tomatoes in smaller pots and have not had much success. Rule of thumb: grow tomatoes in as large of a pot as you can reasonably fit and afford for your space. The bigger the pot, the better the plant.
Choose Container-Friendly Tomatoes:
If you can help it, choose a small, determinate tomato variety for your pots. I recommend Orange Hat tomatoes and Micro Tom for potted plants.
Create the Richest Soil Possible:
Tomatoes grown in pots are going to need more than just a standard bag of potting soil. For the healthiest plants with the biggest fruit, you're going to need to amend the soil with additional nutrients like compost, worm castings, mycorrhizae, and Epsom salts. I also recommend a weekly application of an organic liquid fish emulsion fertilizer.
Sun, Water, and Mulch:
You'll want to place your tomato plants in full sun as tomatoes love warm sunny days. However, on hot sunny days, your tomato plants will gulp up almost all of the water available in the container. This means that you may need to water your potted tomato plants every single day during the hottest summer months. Underwatering your tomato plants can seriously stress them out and stunt their growth, while overwatering can cause disease and stress as well. There are two things that you can do to maintain a nice consistent level of moisture for your tomato plants. First, heavily mulch your tomato pots with 3-4 inches of mulch such as Garden Straw or wood chips. The mulch will help to protect the soil from the direct heat of the sun and slow down evaporation. Second, add an automatic watering globe to each potted tomato plant. Watering globes are relatively inexpensive ways to ensure that your potted plants have the exact amount of water they need: no more, no less. Simply fill up the globe with water and your tomato plant will suck up as much water as it needs. When the globe is near empty, refill it.
Trellising & Support:
All except the smallest determinate tomatoes will need some form of support or trellising. A tomato cage is a great option for this because they fit well in a wide variety of container sizes. Even a simple garden stake placed in the center of the pot will work well. Simply use a string or wire to attach the main stem of the tomato plant to the stake as it grows.
Tomato Plant Care & Maintenance:
Once your tomato plants are in the ground with healthy soil and mulch, all they will need from now on is consistent watering, weekly fertilizing, and pruning. If you really want to grow the biggest tomatoes, read our section below on Advanced Tomato Growing Tips.
Tomato Watering:
Tomatoes need consistent watering throughout the growing and fruit-bearing season. Too much water can increase the likelihood of certain tomato diseases and cause tomato fruit to crack from too much moisture. Underwatering can stress your tomato plants and possibly stunt their growth. To hit the sweet spot, you should invest in drip-irrigation, watering globes, or some form of automatic watering system that can deliver consistent water to the tomato plant. Also, be sure to heavily mulch around your tomato plants with straw, wood chips, or Better Reds mulching film. Tomatoes will need more water on the hottest days during the growing season and less during fruit-set towards the end of summer. Don't trust online estimates of how much water your plants will need. This highly depends on your specific growing conditions.
Tomato Fertilizing:
With healthy soil amended with compost, worm castings, and Epsom salts, tomato plants shouldn't need much more fertilizing throughout the growing season. However, I do like to boost my plants with a weekly dose of organic liquid fish emulsion because I've noticed that I get way bigger fruit and healthier plants when I do this.
Tomato Pruning:
For healthy plants that produce huge fruit, you are going to need to consistently prune your tomato plants. This topic is too big for this little bullet point, so please refer to our Advanced Tomato Growing Tips for more information. Yes, you can just skip pruning and let your tomato plants grow wild. But, be prepared to have to wade through a jungle to find your tomato fruit come harvest time.
Tomato Trellising:
Tomato plants have the tendency to grow into massive plants. Massive plants need massive support. This is one area of tomato growing that I struggled with for many years. Finding the right trellising system that allows for easy maintenance of your tomato plants is critical. Again, this topic is more than I can fit in this section, so refer to the Advanced Tips below.
Organic Liquid Fish
Organic Liquid Fish Fertilizer
GS Plant Foods Organic Liquid Fish is an all-natural high quality fresh fish liquid fertilizer that gives excellent plant growth, rebuilds soil, and offers higher production yields. This is what I use for all of my garden plants with huge results!
Advanced Tomato Growing Tips
Now that we've covered the basics of how to grow tomatoes, it's time to discuss more advantage care and maintenance strategies. These tips are going to cover the three most important advanced tomato growing techniques: pruning, trellising, and propagating tomatoes. You don't necessarily have to do these, but doing so will definitely increate your tomato harvest tremendously.
Pruning Tomatoes
There is a lot of controversy around tomato pruning. Do you prune suckers or leaves? How much should you prune? Does it actually contribute towards bigger tomato fruit? For years, I diligently followed the generic advice of gardeners to prune away tomato suckers. While this definitely created a more manageable plant, my tomato yields were always very disappointing. A few years ago, I dove deep into tomato growing literature and figured out exactly what was happening and why my tomato plants weren't producing a ton of fruit. Since then, I've used what I've learned and tweaked my tomato pruning techniques. The result? A ton of big, juicy, healthy tomatoes!
Here is what I've learned and the exact strategy I use to grow the best tomatoes on the block:
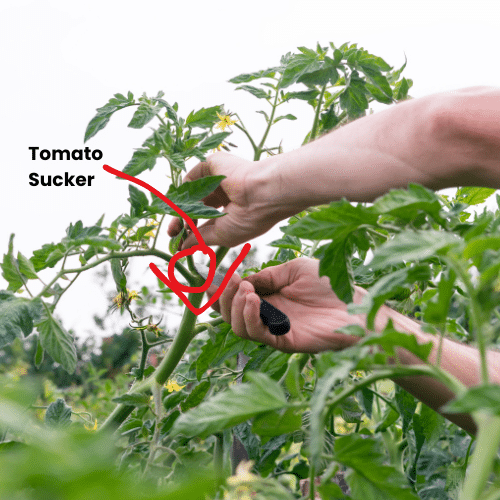

Tomato Suckers. Should You Prune Them?
Tomato suckers are offshoots of tomato plants. They grow in the space between tomato branches and the main stem (see image above). Tomato suckers produce branches which will produce more flowers and tomato fruit. Popular consensus says that we should prune suckers because they "suck energy" away from the plant and result in smaller tomato fruit. This is the advice that I followed for years and, although I did get larger tomatoes, my harvest was dramatically smaller.
Tomato leaves stems are the parts of the plant that do not produce flowers or fruit. These stems only contain leaves and their main job is to gather energy from the sun to help the plant grow. These leaf stems also consume a fair big of energy from the plant as well as they increase the plant's need for nutrients. If you only prune the leaf stems and leave the suckers, your plant will produce a lot of smaller-sized tomatoes.
The trick? Prune some of each! This strategy leaves some suckers for more fruit and removes some leaf branches to ensure larger fruit.
Pruning Suckers:
Suckers are new tomato plant growth which emerge at the junction between the main branch and a leaf stem. Suckers will produce flowers and fruit. The less suckers, the less fruit. The more suckers, the more fruit, but they will be smaller. Prune anywhere from 50%-75% of the suckers that grow on your tomato plants. Leave a few suckers to grow and add more tomatoes to your plant. To prune suckers, simply pinch or trim them off at the base. Check for new suckers at least once per week.
Pruning Leaf Stems:
Leaf stems or branches are parts of the tomato plant which only produce leaves. By pruning leaf branches, you'll be concentrating the plant's energy into producing big, beautiful fruit. Prune the bottom 50% of leaf stems, making sure to leave a nice canopy of leaf stems towards the top of the plant. The leafy branches at the top will help to provide shade for the tomato fruit below and prevent sun scalding. To prune leaf branches, simply identify branches of the tomato plant which only have large leaves (no fruit or flowers).
Propagating Tomato Plants
Did you know that you can create almost endless tomato plants from just one tomato plant? As it turns out, fruit-bearing branches of your tomato plant can be trimmed and propagated so that they become their own tomato plant! This is 100% not necessary to do, but it's a great way to save money on tomato plants by creating your own from a single plant. Here's how it works:
How to Propagate Tomato Plants

Identify a Fruit-Bearing Stem:
Identify a branch of your tomato plant that is producing flowers. We'll want to use a nice-sized healthy branch for this. Do not cut the main stem! Simply cut the branch off where it meets the main stem of the tomato plant. Also, do not cut off any stems at the top of the plant or else you'll risk "topping off" your tomato plant and stunting its growth.
Sever Once Rooted:
Place the stem into a glass of warm water and place that glass in a sunny location. Cut off any lower leaves which would be submerged or touching the water.
Wait for Roots to Appear:
Within 7-14 days, you should start to see new roots appear at the base of the plant. Once these new roots are at least 2 inches long, you can safely transplant your new tomato plant into the ground!
Transplant Your New Tomato Plant:
Follow the instructions above to transplant your new rooted tomato plant into the ground.
Trellising Tomato Plants
For the healthiest tomato plants and easiest harvest, it is highly recommended that you trellis your tomato plants. Trellising is the act of providing vertical support for your tomato plants. Whether you are growing one or many tomato plants, trellising your plants will make your life so much easier. Without proper support, your tomato plants will sprawl all over the ground and your garden where they have a higher likelihood of exposure to fungus, pests, diseases, and foot traffic. There are many ways to trellis your tomato plants and some methods are better than others. For more details on the different types of tomato trellises and their pros/cons, check out my article specifically on How to Trellis Tomato Plants.
Better Reds for Tomatoes
Red Mulching Film For Tomatoes
Did you know that surrounding your tomatoes with red mulch increases yields by up to 20%? The best kept secret for mega tomatoes is red mulch!
Tomato Companion Plants
There is a lot of talk about companion planting. Over the years, I've tried many companion planting strategies. Overall, I've found that most companion planting advice doesn't really work as stated. For example, it is said that dill plants help to repel aphids from tomato plants. I once planted my tomatoes in a garden bed filled with dill only to find both my dill and tomato plants covered in aphids! Additionally, there isn't any scientific evidence that companion planting actually works as stated. There are, however, certain combinations of plants that work well together. Carrots, for example, are a great companion to tomatoes because they do not interfere with each other's growth. Additionally, there are plants which will inhibit or interfere with the growth of your tomato plants (like potatoes and fennel). For more information on companion planting and which plants work well as tomato plant neighbors, check out our article on Tomato Companion Plants.
Harvesting, Storing, & Preserving Tomatoes
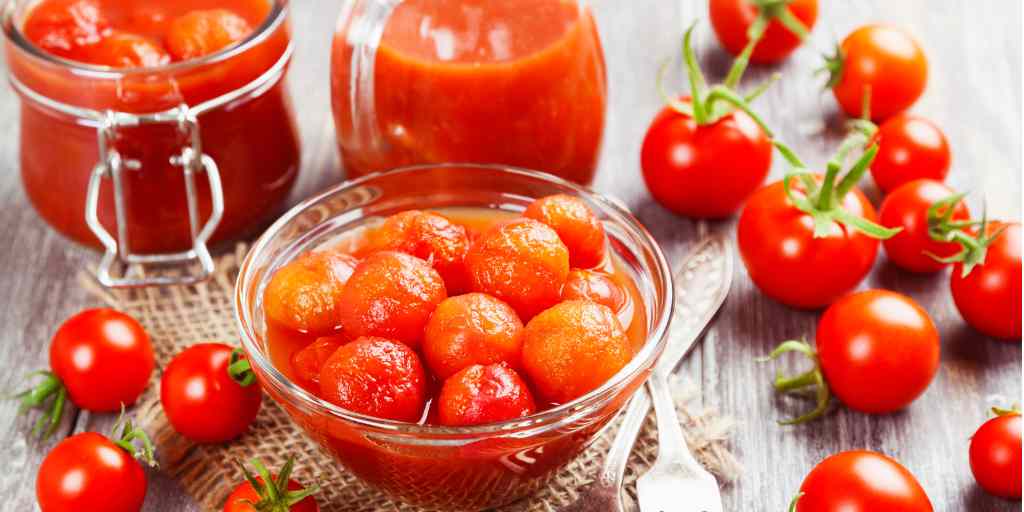

You've finally reached the moment you've been waiting months for--harvesting your beautiful tomatoes! If you've done your job right, then you should be in for a bumper crop of tomatoes. Soon, your countertops will be overflowing with your daily harvests. Your mood may quickly change from joy to borderline panic as you wonder "what will I do with all of these tomatoes?!" Don't worry, there is no such thing as "too many tomatoes" as there are dozens of ways to enjoy and preserve your abundant tomato harvests. Here are some of my favorite ways to enjoy a bounty of tomatoes:
Fresh Tomatoes:
Obviously, one of the best ways to enjoy homegrown tomatoes is to eat them fresh. Fresh tomatoes make amazing additions to salads, quiches, frittatas, sandwiches, pasta dishes, salsas and more! There is no need to refrigerate fresh tomatoes. Simply leave them on your kitchen countertop until you are ready to use them. Even better, if you harvest tomatoes at first-blush or at the breaker stage, then you can leave your tomato on the counter for several weeks while they fully ripen.
Frozen Tomatoes:
Freezing tomatoes is my favorite thing to do when I am overwhelmed with my tomato harvest. Tomatoes can be frozen for about six months. The benefit of freezing tomatoes is that it is super easy to remove their skins once they thaw. Typically, tomatoes need to be blanched in hot water in order to remove their skin; which is a time consuming process. When frozen, simply leave the tomatoes out to thaw for about 30 minutes and their skins just slip right off. This makes it radically easier to make pasta sauce or canned whole tomatoes.
Dehydrated or Freeze Dried Tomatoes:
If you own a dehydrator or freeze-drier, it is super easy to preserve your tomato harvest for years to come. You can use your dehydrator to make tomato paste and "sun-dried" tomatoes. A freeze-drier enables you to make tomato powder which can be added to foods directly or reconstituted with water to create tomato juices, pastes, or sauces.
Canning Tomatoes:
There are lots of ways to can tomatoes. I like to make canned diced tomatoes, canned whole tomatoes, and canned salsa. Tomatoes can be canned using the water-bath method. Once canned, your tomatoes are shelf stable for 2 years or more!
Tomato Growing & Maintenance Calendar
Here's a helpful little calendar for growing tomatoes for each zone by month. Please note, this calendar is for outdoor tomatoes. If you have a greenhouse, then you're growing timeline can get pushed back a little. For example, I live in zone 6 and like to start seeds for my greenhouse tomatoes in February and set the plants out in the greenhouse sometime in late March. Without a greenhouse, I would start my tomato seeds in late March or even Early April and transplant in May.
January-February
Zones 8,9,10: January is a good month to start your tomato seeds indoors. Zone 8 should probably wait until February just to be sure, but January is possible depending on your exact weather conditions.
Zones 3-7: Unless you have a greenhouse, hold off on starting any tomato seeds until March and April. Now is a good time to shop for tomato seeds, buy any seed starting equipment that you mayneed, and make plans for your garden.
March - April
Zones 8,9,10: Transplant your tomato seedlings outdoors in March/April after your zone's specific last frost date has passed.
Zone 3-7: Mid to Late March is a good time to start tomato seeds indoors for most of these zones. For colder zones, like zone 3 and 4, you'll need to pay close attention to your spring weather as you are prone to late frosts. You may need to wait until early April to start your tomato seeds indoors. Nighttime temperatures should be consistently above 40F (50F ideally) before setting out tomato seedlings.
May-June
All Zones: At this point in the season, almost all zones should be able to transplant their tomatoes outdoors. For the coldest zones, there may be nights where you have to cover your tomato plants with a row cover if temperatures dip below 40F at night. By late June, every zone should be in the clear!
July - August
All Zones: The hottest summer months are here and your tomato plants will need consistent watering to be able to thrive during these extra hot days. Check your plants and soil moisture levels daily during this time. If your plants start to look droopy, then the need more water than you've been giving them. By now, your plants should have an abundance of flowers. Warmer zones may have already enjoyed many fruit by now while cooler zones may be waiting on the first fruit to ripen.
Zones 8,9,10: You guys can start another round of tomato seeds indoors in August for a fall crop. Your summer tomatoes may be undergoing a fair bit of stress right now with daytime temperatures reaching all-time highs. Provide some shade to your tomato plants during these hot months and be sure to keep up with watering.
September - October
Zones 3-7: Summer is winding down and the cooler night may be taking a toll on your tomato plants. September is usually peak harvesting season for tomatoes in cooler zones. As October rolls around, you may need to begin covering your tomato plants at night when temperatures dip below 40F. At this point in the year, I usually begin to prune away new tomato plant flowers (because there is no way those fruit will have time to mature before winter) to focus the plant's energy on ripening existing fruit.
You can start taking down your tomato plants after first frost. Pick any tomatoes with color and allow them to ripen on your countertop. Some green tomatoes can be force ripened by placing them in a bag with an apple or banana. You can also make green tomato salsa with your green tomatoes.
Zones 8-10: As your summer plants are winding down, your fall tomato plants are ready to be transplanted outdoors for a fall run.
November - December
Zones 3-7: Tomato season is officially over with the onset of fall frosts. Clean up old plants and take notes on what worked and didn't work this season. Make plans to improve your tomato growing next year!
Zones 8-10: You should be enjoying the abundance of fall and winter tomatoes. These months are typically better for the hottest zones (9-10) to grow tomatoes as the hottest months of the summer may prevent your tomatoes from setting fruit.
Tomato Diseases, Pests, & Troubleshooting
"What's wrong with my tomato?" Inevitably, during your time as a tomato farmer, you will run into issues with your plants. This happens to even the most seasoned farmers and gardeners. So, don't worry. In most cases, the problem comes down to nutrient deficiencies, poor watering habits, or a sneaky little pest. Luckily, most tomato problems can be solved quickly and still result in big beautiful tomato fruit. Let's explore the most common tomato issues and how to solve them.
Note: This is just a small sampling of tomato problems. For a comprehensive list of common tomato problems, I highly recommend checking out a guide by the University of Maryland's Extension Program.
Tomato Diseases & Deficiencies
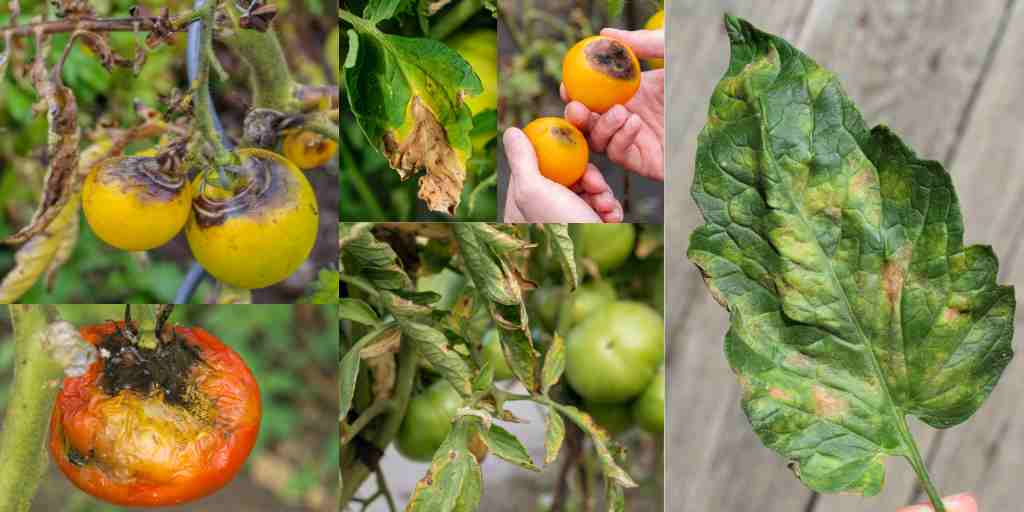

Before we get started on tomato diseases and deficiencies, I want to take a moment to talk about prevention. It is much better to cultivate good gardening habits to prevent disease and deficiencies than it is to treat them. Good habits for tomatoes include:
- Pruning the lower branches of your tomato plant so that no leaves touch the soil (this helps to prevent the spread of soil-borne fungal diseases).
- Pruning and spacing your tomato plants to create better airflow and sunlight exposure throughout the plant to prevent bacterial and fungal diseases.
- Purchasing tomato varieties which have resistances to certain conditions such as Fusarium wilt and early blight.
- Amending your soil with proper organic nutrients before planting tomatoes to ensure strong plants.
- Ensuring proper soil moisture and temperature to reduce plant stress. A stressed plant is far more susceptible to pest and disease.
Fusarium Wilt:
Tomato plants are susceptible to soil-borne fungal diseases fall Fusarium wilt. With fusarium wilt, the symptoms become apparent when your tomato fruit begin to ripen. Symptoms include:
- Yellowing of leaves on the lower part of the plant or on one side of the plant or branch.
- To test for fusarium wilt, lightly scrape the top layer of the infected plant stem. If the tissue just under the stem is brown, this is a tell-tale sign of fusarium wilt.
Solution: No known cure. Remove and destroy diseased plants. Sanitize all gardening tools to prevent the spread of the fungus to other plants. Purchase tomato seeds with resistance to fusarium wilt.
Bacterial and Verticillium Wilt:
Tomatoes can wilt for a variety of reasons which include stress from hot weather or poor watering habits. Here are some signs that your plant is suffering from bacterial or verticillium wilt:
- Verticillium wilt: a slow progressing wilt and yellowing of leaves which affects the entire plant (not just one section of the plant as with fusarium wilt) starting from the bottom and moving upwards.
- Bacterial wilt: a yellowing and wilting of leaves which starts from the top of the plant and moves downward (unlike fusarium and verticillium wilt which start from the bottom and move up).
Solution: No cure. Fungus can remain in the infected soil for years. Destroy infected plants. Choose a new planting location, select a resistant variety, or both.
Nutrient Deficiencies:
Nutrient deficiencies can usually be spotted early and the plant can be saved with the addition of proper nutrients. Here is a sample of common nutrient deficiencies and signs in tomato plants:
- Low Phosphorus: Purple color on the underside of tomato leaves. Most commonly seen in tomato seedlings.
- Low Magnesium: Yellowing between the veins on older leaves and then progressing to newer leaves.
- Low Nitrogen: Pale green or light yellow older leaves. Plant may appear smaller or have weakened growth.
- Low Potassium: Yellowing of the edges of tomato leaves. Yellow and green spots on fully ripened fruit.
- Low Calcium: Poor calcium in tomato plants often presents itself on the fruit as "blossom end rot" which is a rot that effects the bottom or blossom-end of the tomato fruit.
Solutions:.
- Low Phosphorus: Usually goes away when seedlings or transplants establish their roots in their new garden soil. If the problem persists, amend soil with Rock Phosphate.
- Low Magnesium: Create a foliar spray made with 1 tsp Epsom Salts dissolved in a quart of water. Spray plants once every two weeks until symptoms cease.
- Low Nitrogen: Amend soil with blood meal, manure, and/or a weekly dose of organic liquid fish fertilizer.
- Low Potassium: Amend soil with langbeinite or potash.
- Low Calcium: Low calcium in tomato plants is likely not caused by low calcium in the soil (thus, amending the soil with calcium is not the most effective solution). Instead, calcium deficiencies are typically caused by the plant's inability to uptake calcium from the soil. This is caused by improper and inconsistent watering habits. Ensure that you are giving your tomatoes consistent water with a drip irrigation system or watering globe.
Tomato Pests
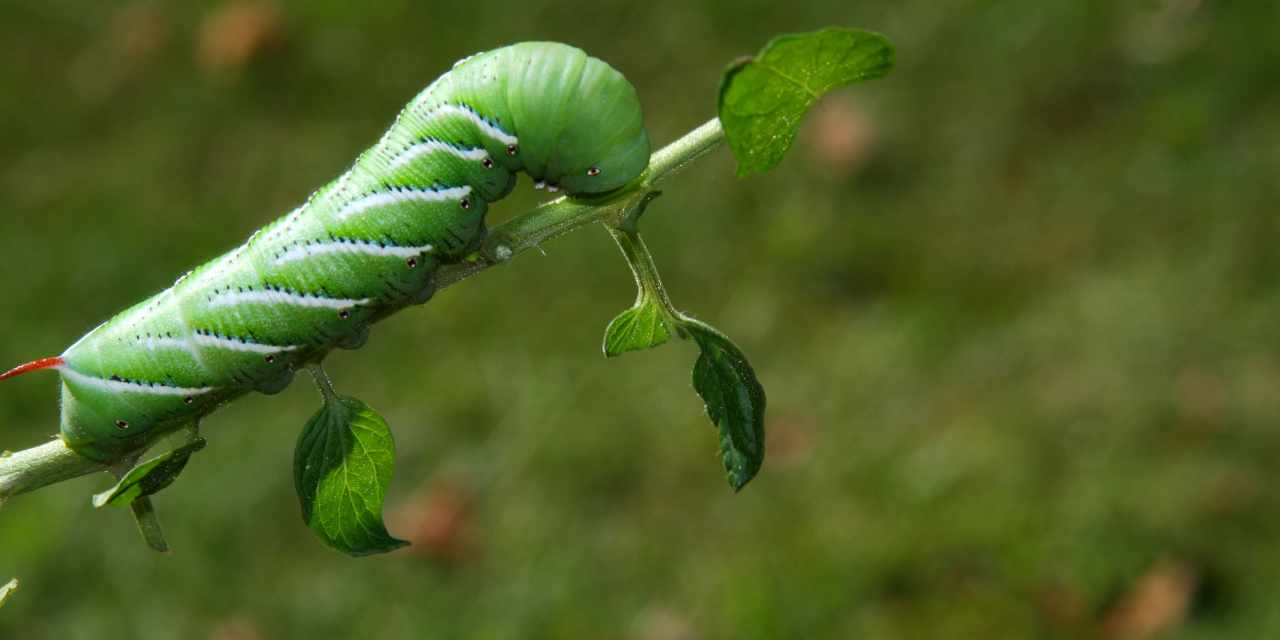

Humans aren't the only ones who can't wait to take a bite out of a big juicy tomato. Tomato pests range from small aphids to larger pests such as squirrels, birds, and the dreaded tomato hornworm. Unlike fungal diseases, tomato pests are much easier to deal with and can be quickly thwarted. Stay vigilant and monitor your garden regularly for signs of pest attacks. Here is a table containing information on how to identify certain tomato pests and remove them:
| Pest | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Spider Mites | Small spider-like bug which suck chlorophyll from leaf tissues of tomato plants. Leaves turn yellow and eventually brown and die. Can be spotted by small webs formed on and around the plant. | Typically caused by dry and hot conditions. Increase the humidity by hosing the plants off. Clean or remove infected leaves. Spray with a solution of neem oil and soapy water. |
| Flea Beetles | Small tiny holes in leaves caused by very small black bugs which jump like fleas. | Use row covers in the early spring when flea beetles are most active. Spray a solution of kaolin clay and water on vulnerable plants which repels flea beetles. Dust plants with diatomaceous earth. |
| Tomato Hornworm | Very large moth caterpillars which eat entire tomato leaves and branches. | Examine plants regularly and remove hornworms by hand. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Growing Tomatoes
Why Are My Tomato Leaves Turning Yellow?
Yellowing tomato leaves can be a sign of fungal or bacterial infections, poor nutrition, or pests. Refer to our guide on Tomato Diseases to figure out the signs and symptoms of each ailment to determine the specific cause of your tomato plants yellow leaves.



